SEO Guide for Beginners
There's a lot of bad information and shady salesmen for SEO, I'm hoping this introductory guide will help educate small business owners and help them do their own SEO.
Disclaimer: I'm not an SEO expert nor do I offer any SEO services. This article is an explanation of SEO how I know it as a web developer and is therefore my opinion.
What exactly is SEO?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization. But what exactly does that mean? It's another way of saying you want to improve your website's search rank on Google. Why am I only mentioning Google and not other search engines? Let's be honest, Google is the only search engine that matters right now. So from now on, the only search engine and SEO we're talking about is for Google.
Why does SEO often get a bad rep?
The reason why SEO is often filled with shady people, bad info and spam is because SEO is a results driven process, where the rules of the game are hidden and difficult to measure. Good SEO takes months to years to fully take effect and this tempts people into taking shortcuts. What happens if you try to take a shortcut anyway? Well Google has some of the world's best engineers and a near unlimited amount of money, so any attempts to subvert the system will probably be removed and possibly punished.
How do you do SEO?
This is a tricky question to answer and probably where I will get the most amount of disagreement. In general you want to make it as easy as possible for Google to look through and store your website (aka crawling or indexing). An important thing to note is SEO is Google's game and you should play by their rules. If you keep this in mind, you'll find it makes everything easier. For this section I'll split it into two parts.
Planning and Analytics
A common strategy for SEO is to target keywords, but how do you go about doing that? Before I can tell you, I need to talk more about keywords. Keyword analytics are not my area of expertise so I'll keep it brief.
Keywords are words what you type into Google and what allows Google to serve relevant content. Naturally there are high competitive keywords and low competition keywords. Low competition keywords are often called long-tailed keywords and it is a common strategy to target long-tailed keywords.
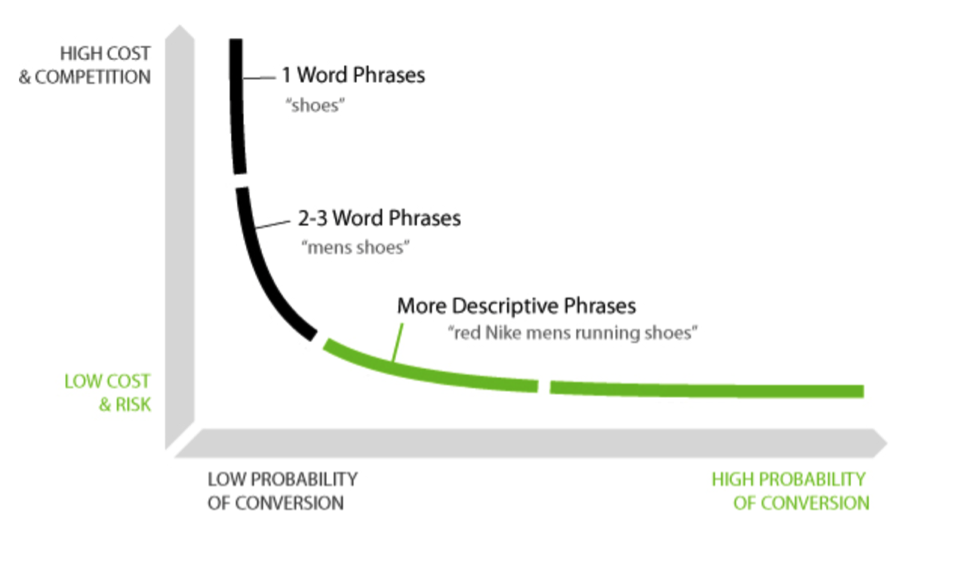
Conversion is when a user successfully does what you want, such as buying a product or signing up for a newsletter.
So how do you tell these keywords apart by competition? Plenty of people use sites like SEMRush. But generally the lower the amount of words and the more general they are, the more competitive they are and the higher the words, the more descriptive and less competitive they are. For example, keywords like "real estate agent" are probably highly competitive and too broad but a keyword like "san gabriel property under 700000" would be considered a long-tailed keyword. If you're having trouble coming up with keywords, sites like UberSuggest are often used.
You can also use tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console to help you see what current users are searching for when they find your website.
Implementing SEO
For being able to actually apply SEO, you should have at least some technical skills or know someone who does. Here are some of the factors that Google takes into account when crawling your website for SEO.
- Site Speed (How fast it loads on mobile in particular)
- Putting keywords in certain places like your page's header and title
- Quality of the content (No duplicate content or spam)
- Having a well structured website including things like a meta title, meta description and alt values for images
- How many other websites link back to your site (also called backlinks)
- How reputable (or authoritative) the other websites that link to you are
- Having certain files like a sitemap.xml and a robots.txt in your website
In recent years, the measurement of site speeds have changed and loading speed on desktop is no longer enough. With almost 50% of all web traffic coming from mobile, Google has now weighed mobile site speed heavily for SEO. Which means website performance is more important due to slower internet speeds from mobile. There are tools like Google's PageSpeed Insights which will help audit your website and give you tips on how to improve your site speed.
When it comes to putting in your targeted keywords in your website, where you put it matters too. Titles and headers are often the suggested place to put them. However, whether Google weighs content more heavily in places like titles, domains and headers is highly debated and often anecdotal.
As for the actual content on a page, Google tries to look for high quality content and tries to punish those that spam for SEO. High quality content can include content that gives users exactly what they're looking for and well written informational blogs and etc. Bad content on the other hand, can be things like duplicate content (multiple identical websites), SEO spam (unreadable text and repeated words).
In addition to good content, good SEO includes a meta title and meta description. If you look a Google search result, the name and description actually comes from the meta title and description which is why it's important. Good SEO also includes alt image text which is just text that is displayed when an image fails to load or if a user is using a handicap program. Alt tags are also important for ADA compliance, which goes hand in hand with SEO.
Perhaps one of the most important parts of SEO are the links that link to your website. When a website links to another page or site, they usually pass what is often called link juice, which is the passing of a reputation or value from one site to another. Having a lot of websites that link to your website is great, but perhaps what matters more is the quality and reputation of the websites that are doing the linking. Also known as authority websites, these websites have a good reputation, provide factual information and are generally seen as trustworthy. Being linked from an authoritative website is probably worth more than a number of non-authority websites. For example, being linked from an article in The New York Times will be way more beneficial to SEO than being linked from a few no-name websites. Thus, it's greatly beneficial to get your brand out in news outlets, blogs/articles and industry leaders.
Lastly, websites having a sitemap.xml and robots.txt helps Google crawl your website more easily. As a rule, you should be making it as easy as possible for Google to index your website. A sitemap.xml is a file that maps all the pages of your website and a robots.txt tells Google what to index and what not to index. Both should be accessible at yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml and yourwebsite.com/robots.txt. You can see an example from my own sitemap.xml and robots.txt.
Questionable strategies
When it comes to SEO, not everyone plays by the rules. Here are some strategies I've never tried myself but heard others talk about doing.
- Buying expired domains and making them link to or redirect to your website
- Paying for SEO services that will try to spam backlinks to your website
- Hacking websites and inserting content for someone else's SEO. This goes hand in hand with paying for mass backlinks.
- Spamming intentionally bad SEO for your competitor's websites in order to lower their search ranking (You need to learn how to disallow links in order to combat this if it happens to you).
Final thoughts
Hopefully if you reach this point you understand SEO a bit more. There is a wealth of information beyond what I've mentioned here, but SEO is a long term investment so it's okay to take it slow. Try your best to do SEO properly as taking a shortcut will mostly likely not work out in the long run.
Here is some detailed reading for those that want to know more: